通过小菊的语义分割1🌼,我们已经知道了语义分割其实就是像素级的分类任务,也就是说它要做的是给每一个像素点进行分类,那我们具体应该怎样实现这个特殊的分类任务呢?————不急,我们先来看一下普通的图像分类任务是怎样实现的
0. 图像分类任务实现原理
其实我们的语义分割——像素级分类和我们的普通图像分类任务还是非常相似的,只不过是一个给像素点进行分类,一个给整个图像进行分类,它们的标签处理方式和最后的损失计算都是非常相似的。
首先,我们假设有这样一堆图片,里面总共有3个类——猫,狗和狼,那么我们定义标签的时候可以将猫作为第0类,狗是第1类,狼是第2类,然后给它们转换成分类常用的one-hot编码格式,如下所示:
类别 标签 one-hot
猫 0 [1, 0, 0]
狗 1 [0, 1, 0]
狼 2 [0, 0, 1]
我们把每一张图片和它的one-hot编码格式标签对应起来,就可以用于后面的损失函数计算了。
接下来我们再看看我们的分类网络的输出是怎样的。分类网络的输出是一个一维数组[…],具体数组里面有几个元素和我们要分的类别有关,我们这里分3类,数组的长度就为3————[x0, x1, x2],之后我们Softmax([x0, x1, x2]),得到[p0, p1, p2],其中p0+p1+p2=1,p0代表的是图像为第0类的概率,p1代表的是图像为第1类的概率,以此类推。最大概率对应种类就是分类网络预测的图像的种类。例 我们将标签为[0, 1, 0]的图像输入到分类网络得到输出[0.1, 0.7, 0.2],其中最大概率0.7对应的类别为1,则分类网络任务该图像为狗。
最后我们来看一下分类网络损失的计算:交叉熵
\[\large loss = - (\sum\limits_{i=1}^N y\_true_i * ln( y\_pre_i )) \tag {1}\]其中 $0 < y_pre_i <= 1$。因为我们的y_true只有一个为1,其余全为0,带入可得我们的损失为 loss = - ln( y_prei ),带入我们上边的例子就是loss = -ln(0.7),ln函数在(0,1]为增函数,加上负号为减函数,也就是说我们的分类网络只有提高图像分类正确的概率,我们的loss才会减小。
损失理解:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
import numpy as np
import math
import tensorflow.keras.backend as K
# 类别 标签 one-hot
# 猫 0 [1, 0, 0]
# 狗 1 [0, 1, 0]
# 狼 2 [0, 0, 1]
labels = ['0', '1', '2']
y_true = ['1', '0']
y_pred = [ [0.2, 0.6, 0.2],
[0.3, 0.3, 0.4] ]
sk_log_loss = log_loss(y_true, y_pred, labels=labels)
print('sk_log_loss:', sk_log_loss)
def crossentropy(y, x):
return -(y * np.log(x))
y_true = np.array([[0, 1, 0], [1, 0, 0]])
y_pred = np.array([[0.2, 0.6, 0.2], [0.3, 0.3, 0.4]])
print("Keras:", K.categorical_crossentropy(K.constant(y_true), K.constant(y_pred)))
loss1 = 0.0
loss2 = 0.0
loss1 = np.array(loss1).astype('float32')
loss2 = np.array(loss2).astype('float32')
for i in range(3):
loss1 += crossentropy(y_true[0][i], y_pred[0][i])
loss2 += crossentropy(y_true[1][i], y_pred[1][i])
mean_loss = (loss1 + loss2) / 2
print("ours :", loss1, loss2, mean_loss)
sk_log_loss: 0.8573992
Keras: tf.Tensor([0.5108256 1.2039728], shape=(2,), dtype=float32)
ours : 0.51082563 1.2039728 0.8573992
看懂了普通的图像分类任务之后,再看我们的语义分割,其实就是给每一个像素点对应一个one-hot编码标签,之后我们的语义分割网络的输出和分类网络的输出也是一样的,会输出每一个像素点对应每个类别的概率。如下所示:
Output Label
[[0.4, 0.3, 0.3], [[1, 0, 0], # 第1个像素点
[0.7, 0.2, 0.1], [1, 0, 0], # 第2个像素点
[0.8, 0.2, 0.0], [1, 0, 0], # 第三个像素点
[0.8, 0.1, 0.1], [1, 0, 0], # 第四个像素点
... ...
]
接下来就让我们看一下它在语义分割中是怎样具体实现的吧
1. 数据预处理
思路: 读取train.txt文件,获取训练图像及对应标签的文件路径,读取图像,将图像转化为tensor之后,resize调整图像尺寸大小并进行归一化处理,之后也可通过旋转,色偏,增加噪声等方式进行数据增强。注意要保证图像和标签的处理一致。
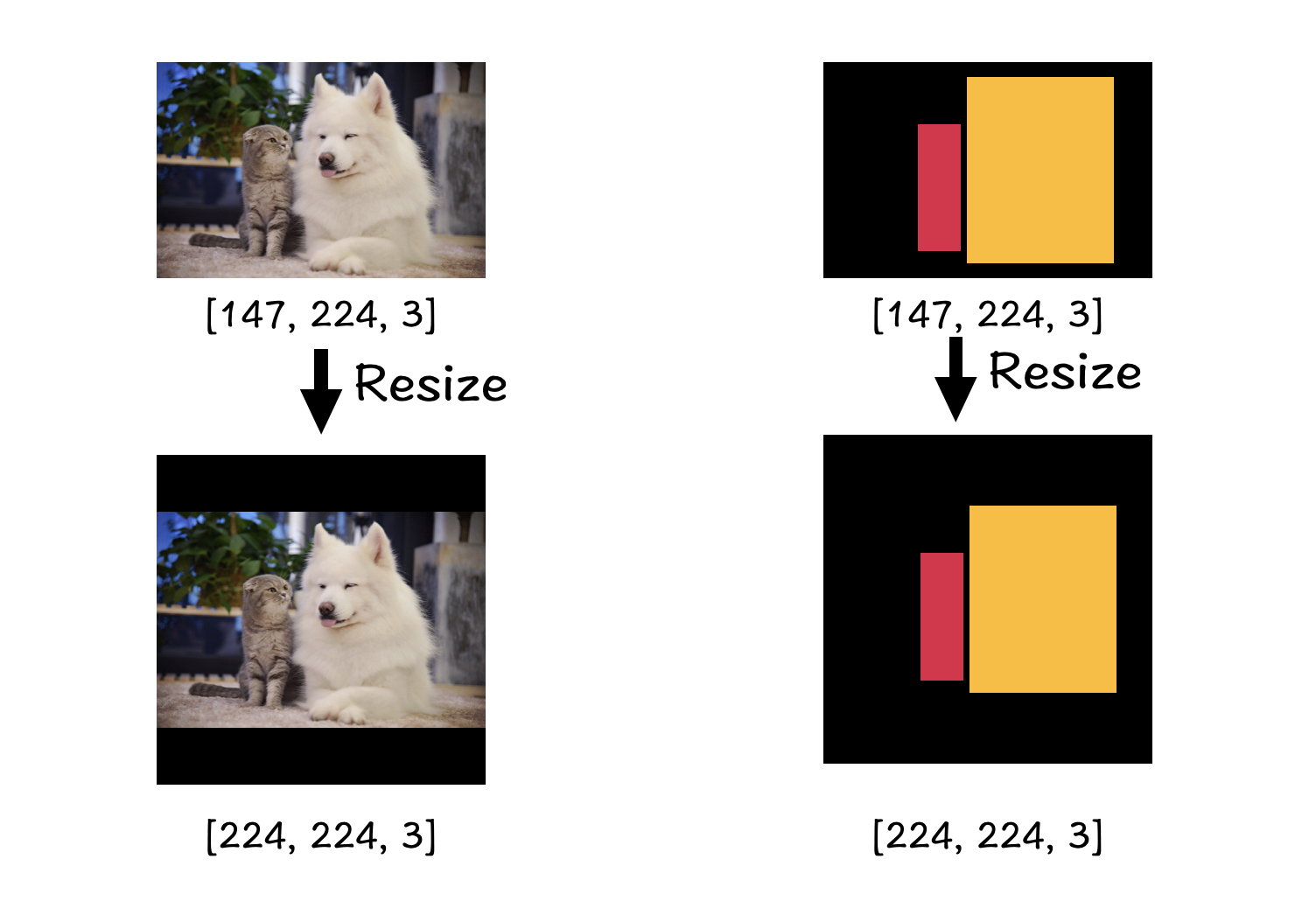
padding可以使图像在resize时不失真
2. label map 标签映射

如图就是我们的语义分割标签图像,相同颜色(像素值)的像素点代表的是同一类物体。假设像我们这个标签图像所展示的那样,我们需要分割出来图片中的猫和狗,那对我们的语义分割任务来说就是总共要分3类:0 背景;1 猫;2 狗;因此,我们需要创建一个[Height, Width, N_classes]数组来表示每一个像素点的类别;如下图所示:

label[0, 0] = [1, 0, 0] 说明[0, 0]位置是背景,label[1, 1] = [0, 1, 0]说明[1, 1]这个像素点属于猫。我们Reshape之后好像更方便大家理解:
1
seg_labels = np.reshape(seg_labels, (-1,NCLASSES))
one-hot 编码
[[1, 0, 0],
[1, 0, 0],
[1, 0, 0],
[1, 0, 0],
[1, 0, 0],
[0, 1, 0],
[0, 0, 1],
[0, 0, 1],
...
]
这就是我们最后用来和预测结果计算损失的数据啦🌼相信大家对为什么这样做还有点云里雾里的感觉,那么接下来就让我们揭开语义分割的神秘面纱吧🌼
3. 像素级分类原理
了解完lable的具体格式之后,我们来看一下网络的最后几层设计:
1
2
3
x = Conv2D(n_classes,(1,1), padding='vaild' )(x)
x = Reshape((-1,n_classes))(x)
output = Softmax()(x)
这个和我们label的处理是一致的,输出的是每一个像素点属于哪一类的概率,如下图:

tensor表示:
Output Label
[[0.4, 0.3, 0.3], [[1, 0, 0],
[0.7, 0.2, 0.1], [1, 0, 0],
[0.8, 0.2, 0.0], [1, 0, 0],
[0.8, 0.1, 0.1], [1, 0, 0],
... ...
]
将我们处理之后的label和预测得到的结果传给我们的损失函数就能计算出loss了,这样我们就实现了像素级的分类————也就是语义分割了🌼
帮助理解标签的处理
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
from PIL import Image
from keras.utils import to_categorical
CLASSES = {
# 默认背景为0
76 : 1, # 建筑物
150 : 2, # 植被
255 : 3,# 道路
}
NCLASSES = 4
HEIGHT = 2
WIDTH = 2
labels = [[25, 76],
[150, 255]]
labels = np.array(labels).astype('int')
labelmap = np.zeros((int(HEIGHT), int(WIDTH)))
for k in CLASSES:
labelmap[(labels == k)] = CLASSES[k]
labelmap = np.reshape(labelmap, (-1, 1))
labelmap = to_categorical(labelmap, NCLASSES)
print(labelmap)
下面是包含了数据预处理,损失定义等整个模型训练过程的train.py文件,大家稍作修改就可以训练自己的语义分割模型了🌼
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
import numpy as np
from PIL import Image
import keras
from keras import backend as K
from keras.optimizers import Adam
from keras.layers import Lambda
from keras.callbacks import TensorBoard, ModelCheckpoint, ReduceLROnPlateau, EarlyStopping
# 标签像素值对应的物体类别, 0为背景
CLASSES = {
'[0 0 0]' : 0, # 背景
'[7 7 7]' : 1,
'[26 26 26]' : 2,
}
NCLASSES = 2
HEIGHT = 576
WIDTH = 576
BATCH_SIZE = 2
# train.txt和val.txt的文件路径
path_train_txt = ''
path_val_txt = ''
# train的图像和标签路径
path_Xtrain = ''
path_Xlabel = ''
# val的图像和标签路径
path_Yval = ''
path_Ylabel = ''
# labels映射
def label_map(labels):
labelmap = np.zeros((int(HEIGHT),int(WIDTH),NCLASSES))
for h in range(int(HEIGHT)):
for w in range(int(WIDTH)):
if str(labels[h, w]) in CLASSES.keys():
c = CLASSES[str(labels[h, w])]
else:
c = 0
labelmap[h, w, c] = 1
return labelmap
def data_generator(mode):
assert mode in ['train', 'val'], \
'mode must be ethier \'train\' or \'val\''
if mode == 'train':
with open(path_train_txt, 'r') as f:
lines = f.readlines()
np.random.shuffle(lines)
n = len(lines)
path0 = path_Xtrain
path1 = path_Xlabel
else:
with open(path_val_txt, 'r') as f:
lines = f.readlines()
np.random.shuffle(lines)
n = len(lines)
path0 = path_Yval
path1 = path_Ylabel
i = 0
while 1:
images = []
labels = []
for _ in range(BATCH_SIZE):
if i==0:
np.random.shuffle(lines)
name = lines[i].split(';')[0]
img = Image.open(path0 + '/' + name)
img = img.resize((HEIGHT,WIDTH))
img = np.array(img)
img = img/255
images.append(img)
name = (lines[i].split(';')[1]).replace("\n", "")
img = Image.open(path1 + '/' + name)
img = img.resize((int(HEIGHT),int(WIDTH)))
img = np.array(img)
seg_labels = label_map(img)
seg_labels = np.reshape(seg_labels, (-1,NCLASSES))
labels.append(seg_labels)
i = (i+1) % n
yield (np.array(images),np.array(labels))
# 定义损失函数
def loss(y_true, y_pred):
crossloss = K.binary_crossentropy(y_true,y_pred)
loss = K.sum(crossloss)/HEIGHT/WIDTH
return loss
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 用于最后保存模型的路径
log_dir = ''
# 创建模型
model = Net()
# 获取训练样本和验证样本的数目
with open(path_train_txt, 'r') as f:
lines = f.readlines()
num_train = len(lines)
with open(path_val_txt, 'r') as f:
lines = f.readlines()
num_val = len(lines)
# 设置学习率下降方法,val_loss验证损失连续5个epoch不下降就让学习率减半
reduce_lr = ReduceLROnPlateau(
monitor='val_loss',
factor=0.5,
patience=5,
verbose=1
)
# 是否需要早停,当val_loss一直不下降的时候意味着模型基本训练完毕,可以停止
early_stopping = EarlyStopping(
monitor='val_loss',
min_delta=0,
patience=10,
verbose=1
)
# 设置损失,优化器
model.compile(loss = loss,
optimizer = Adam(lr=1e-3),
metrics = ['accuracy'])
print('Train on {} samples, val on {} samples, with batch size {}.'.format(num_train, num_val, BATCH_SIZE))
# 开始训练
model.fit_generator(data_generator('train'),
steps_per_epoch=max(1, num_train//BATCH_SIZE),
validation_data=data_generator('val'),
validation_steps=max(1, num_val//BATCH_SIZE),
epochs=50,
initial_epoch=0,
callbacks=[reduce_lr, early_stopping])
model.save_weights(log_dir+'Dali.h5')
上面的标签处理方便理解,但是时间复杂度高,在cup上处理慢,下面为改进版本:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
from PIL import Image
# import keras
from tensorflow import keras
from tensorflow.keras import backend as K
from tensorflow.keras.optimizers import Adam
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Lambda
from tensorflow.keras.callbacks import TensorBoard, ModelCheckpoint, ReduceLROnPlateau, EarlyStopping
from tensorflow.keras.utils import to_categorical
from models.decoders.segnet import resnet50_segnet
import glob
# logging 模块, 保存日志文件
# ===================>
import logging
logging.basicConfig(filename='./work_dirs/segnet/segnet.log', filemode='a', level=logging.DEBUG, format='%(asctime)s - %(name)s - %(levelname)s - %(message)s')
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
logger.handlers.clear()
logger.setLevel(level = logging.DEBUG)
formatter = logging.Formatter('%(asctime)s - %(name)s - %(levelname)s - %(message)s')
console = logging.StreamHandler()
console.setLevel(logging.INFO)
console.setFormatter(formatter)
logger.addHandler(console)
# <==================
# 标签像素值对应的物体类别, 0为背景
CLASSES = {
# 默认背景为0
76 : 1, # 建筑物
150 : 2, # 植被
255 : 3, # 道路
}
NCLASSES = 4
HEIGHT = 512
WIDTH = 512
BATCH_SIZE = 8
# train.txt和val.txt的文件路径
path_train_txt = './dataset/train.txt'
path_val_txt = './dataset/val.txt'
# train的图像和标签路径
path_Xtrain = './dataset/jpg/'
path_Xlabel = './dataset/png/'
# val的图像和标签路径
path_Yval = './dataset/val_jpg/'
path_Ylabel = './dataset/val_png/'
# labels映射
def label_map(labels):
labelmap = np.zeros((int(HEIGHT),int(WIDTH),NCLASSES)).astype('float32')
for h in range(int(HEIGHT)):
for w in range(int(WIDTH)):
if str(labels[h, w]) in CLASSES.keys():
c = CLASSES[str(labels[h, w])]
else:
c = 0
labelmap[h, w, c] = 1
return labelmap
def data_generator(mode):
assert mode in ['train', 'val'], \
'mode must be ethier \'train\' or \'val\''
if mode == 'train':
with open(path_train_txt, 'r') as f:
lines = f.readlines()
np.random.shuffle(lines)
n = len(lines)
path0 = path_Xtrain
path1 = path_Xlabel
else:
with open(path_val_txt, 'r') as f:
lines = f.readlines()
np.random.shuffle(lines)
n = len(lines)
path0 = path_Yval
path1 = path_Ylabel
i = 0
while 1:
images = []
labels = []
for _ in range(BATCH_SIZE):
if i==0:
np.random.shuffle(lines)
name = lines[i].split(';')[0]
img = Image.open(path0 + name)
img = img.resize((HEIGHT,WIDTH))
img = np.array(img).astype('float32')
img = img/255
images.append(img)
name = (lines[i].split(';')[1]).replace("\n", "")
img = Image.open(path1 + name).convert('L')
img = img.resize((int(HEIGHT),int(WIDTH)))
img = np.array(img)
img = tf.convert_to_tensor(img)
seg_labels = np.zeros((HEIGHT, WIDTH))
for k in CLASSES:
seg_labels[(img == k)] = CLASSES[k]
seg_labels = np.reshape(seg_labels, (-1,1))
seg_labels = to_categorical(seg_labels, NCLASSES)
# print(seg_labels)
labels.append(seg_labels)
i = (i+1) % n
yield (np.array(images).astype('float32'),np.array(labels).astype('float32'))
# 定义损失函数
def loss(y_true, y_pred):
crossloss = K.binary_crossentropy(y_true, y_pred)
loss = K.sum(crossloss)/HEIGHT/WIDTH
return loss
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 用于最后保存模型的路径
log_dir = './work_dirs/segnet/'
# 创建模型
model = resnet50_segnet(n_classes=NCLASSES, input_height=HEIGHT, input_width=WIDTH)
# 获取训练样本和验证样本的数目
with open(path_train_txt, 'r') as f:
lines = f.readlines()
num_train = len(lines)
with open(path_val_txt, 'r') as f:
lines = f.readlines()
num_val = len(lines)
# 设置学习率下降方法,val_loss验证损失连续5个epoch不下降就让学习率减半
reduce_lr = ReduceLROnPlateau(
monitor='val_loss',
factor=0.5,
patience=5,
verbose=1
)
# 是否需要早停,当val_loss一直不下降的时候意味着模型基本训练完毕,可以停止
early_stopping = EarlyStopping(
monitor='val_loss',
min_delta=0,
patience=10,
verbose=1
)
# 设置损失,优化器
model.compile(loss = loss,
optimizer = Adam(lr=1e-3),
metrics = ['accuracy'])
logger.info('Train on {} samples, val on {} samples, with batch size {}.'.format(num_train, num_val, BATCH_SIZE))
# print('Train on {} samples, val on {} samples, with batch size {}.'.format(num_train, num_val, BATCH_SIZE))
# 开始训练
history = model.fit(data_generator('train'),
steps_per_epoch=max(1, num_train//BATCH_SIZE),
validation_data=data_generator('val'),
validation_steps=max(1, num_val//BATCH_SIZE),
epochs=50,
initial_epoch=0,
callbacks=[reduce_lr, early_stopping])
logger.info(history)
model.save_weights(log_dir+'segnet.h5')
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
210
211
212
213
214
215
216
217
218
219
220
221
222
223
224
225
226
227
228
229
230
231
232
233
234
235
236
237
238
239
240
241
242
243
import argparse
import copy
import os
import time
import warnings
from PIL import Image
import torch
import torchvision.transforms as transforms
from torch.utils.data import Dataset, DataLoader
import torch.optim as optim
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import torch.nn as nn
# ===================>
import logging
logging.basicConfig(filename='./work_dirs/segnet/segnet.log', filemode='a', level=logging.DEBUG, format='%(asctime)s - %(name)s - %(levelname)s - %(message)s')
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
logger.setLevel(level = logging.DEBUG)
formatter = logging.Formatter('%(asctime)s - %(name)s - %(levelname)s - %(message)s')
console = logging.StreamHandler()
console.setLevel(logging.INFO)
console.setFormatter(formatter)
logger.addHandler(console)
# <==================
# 标签像素值对应的物体类别, 0为背景
CLASSES = {
'[0 0 0]' : 0, # 背景
'[22 0 255]' : 1, # 建筑物
'[0 255 0]' : 2, # 植被
'[255 255 255]':3,# 道路
}
NCLASSES = 4
HEIGHT = 512
WIDTH = 512
BATCH_SIZE = 8
# train.txt和val.txt的文件路径
path_train_txt = './dataset/train.txt'
path_val_txt = './dataset/val.txt'
# train的图像和标签路径
path_Xtrain = './dataset/jpg/'
path_Xlabel = './dataset/png/'
# val的图像和标签路径
path_Yval = './dataset/val_jpg/'
path_Ylabel = './dataset/val_png/'
# labels映射
def label_map(labels):
labelmap = np.zeros((int(HEIGHT),int(WIDTH),NCLASSES))
for h in range(int(HEIGHT)):
for w in range(int(WIDTH)):
if str(labels[h, w]) in CLASSES.keys():
c = CLASSES[str(labels[h, w])]
else:
c = 0
labelmap[h, w, c] = 1
return labelmap
class MyDataset(Dataset): # 创建类:MyDataset,继承torch.utils.data.Dataset
def __init__(self, datatxt, mode, transform=None):
super(MyDataset, self).__init__()
fh = open(datatxt, 'r') # 打开txt,读取内容
data = []
for line in fh: # 按行循环txt文本中的内容
words = line.split(';') # 通过指定分隔符对字符串进行切片
data.append((words[0], words[1])) # 把txt里的内容读入data列表保存,words[0]是图片信息,words[1]是label
if mode == 'train':
self.path_train = path_Xtrain
self.path_label = path_Xlabel
self.data = data
self.transform = transform
def __getitem__(self, index): # 按照索引读取每个元素的具体内容
fn, label = self.data[index] # fn是图片path
img = Image.open(self.path_train + fn).convert('RGB')
label = Image.open(self.path_label + fn).convert('RGB')
# from PIL import Image
if self.transform is not None: # 是否进行transform
img = self.transform(img)
return img, label # return回哪些内容,在训练时循环读取每个batch,就能获得哪些内容
def __len__(self): # 它返回的是数据集的长度,必须有
return len(self.data)
def main():
# 实例化网络
model = Net()
# print(model)
if torch.cuda.is_available():
model = model.cuda()
train_transforms = transforms.Compose([
transforms.Resize((512, 512)),
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize((0.5, 0.5, 0.5),(0.5, 0.5, 0.5)),
])
val_transforms = transforms.Compose([
transforms.Resize((512, 512)),
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize((0.5, 0.5, 0.5),(0.5, 0.5, 0.5)),
])
train_data = MyDataset(datatxt=path_train_txt, transform=train_transforms)
train_loader = DataLoader(dataset=train_data, batch_size=2, shuffle=True)
val_data = MyDataset(datatxt=path_val_txt, transform=val_transforms)
val_loader = DataLoader(dataset=val_data, batch_size=2, shuffle=True)
optimizer = optim.SGD(model.module.backbone.parameters(), lr=0.001, momentum=0.9, weight_decay=0.0001)
# print('backbone parameters:', model.module.backbone)
num_epoches = 20
image = {}
criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
val_acc_history = []
best_model_wts = copy.deepcopy(model.state_dict())
best_acc = 0.0
# pretrained_dict = torch.load('/content/drive/MyDrive/search/mmdetection/data/resneXt_imagenet.pth')
# model_dict = model.state_dict()
# pretrained_dict = {k: v for k, v in pretrained_dict.items() if 'classifier' not in k}
# for k in pretrained_dict:
# print(k)
# model_dict.update(pretrained_dict)
# model.load_state_dict(model_dict)
for epoch in range(num_epoches):
print('Epoch {}/{}'.format(epoch + 1, num_epoches))
print('-' * 10)
for phase in ['train', 'val']:
if phase == 'train':
model.train() # Set model to training mode
running_loss = 0.0
running_corrects = 0
for i, (imgs, labels) in enumerate(train_loader):
imgs = imgs.cuda(cfg.gpu_ids[0])
labels = labels.cuda(cfg.gpu_ids[0])
# print(labels)
optimizer.zero_grad()
image['img'] = imgs
image['img_metas'] = imgs
outputs = model.extract_backbone(image, optimizer)
loss = criterion(outputs, labels)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
_, preds = torch.max(outputs, 1)
print('loss:', loss.item())
running_loss += loss.item() * imgs.size(0)
running_corrects += torch.sum(preds == labels.data)
# print('{}/{}'.format(i * 50, len(train_loader.dataset)))
epoch_loss = running_loss / len(train_loader.dataset)
epoch_acc = running_corrects.double() / len(train_loader.dataset)
print(' Loss: {:.4f}, acc: {:.6f} , running_loss: {:6f} , len: {:.6f}'.format(epoch_loss, epoch_acc, running_loss, len(train_loader.dataset)))
else:
optimizer.zero_grad()
# if epoch < 10:
# break
model.eval() # Set model to evaluate mode
running_loss = 0.0
running_corrects = 0
for i, (imgs, labels) in enumerate(val_loader):
imgs = imgs.cuda(cfg.gpu_ids[0])
labels = labels.cuda(cfg.gpu_ids[0])
# print(labels)
optimizer.zero_grad()
image['img'] = imgs
image['img_metas'] = imgs
outputs = model.extract_backbone(image, optimizer)
# print(outputs.shape, labels.shape)
loss = criterion(outputs, labels)
_, preds = torch.max(outputs, 1)
running_loss += loss.item() * imgs.size(0)
running_corrects += torch.sum(preds == labels.data)
# epoch_loss = running_loss / 1000.0
# epoch_acc = running_corrects.double() / 1000.0
epoch_loss = running_loss / len(val_loader.dataset)
epoch_acc = running_corrects.double() / len(val_loader.dataset)
print(' Val_loss: {:.4f}, Val_acc: {:.6f} '.format(epoch_loss, epoch_acc))
if epoch_acc > best_acc:
best_acc = epoch_acc
best_model_wts = copy.deepcopy(model.state_dict())
torch.save(best_model_wts, '/content/drive/MyDrive/search/mmdetection/data/middle.pth')
val_acc_history.append(epoch_acc)
print()
print('Best val Acc: {:4f}'.format(best_acc))
torch.save(best_model_wts, '/content/drive/MyDrive/search/mmdetection/data/resneXt_imagenet_338x600_best.pth')
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
